Ever heard someone say, “That word has a negative connotation,” and wondered what that really means?
Language isn’t just about what words literally say — it’s also about what they imply or make you feel. That’s where connotative meaning comes in.
In this article, we’ll explore:
The definition of connotative meaning
Its origin and linguistic background
How it’s used in different contexts
Examples that show how connotations shape communication
Similar terms, common mistakes, and FAQs
📖 What Does Connotative Meaning Mean?
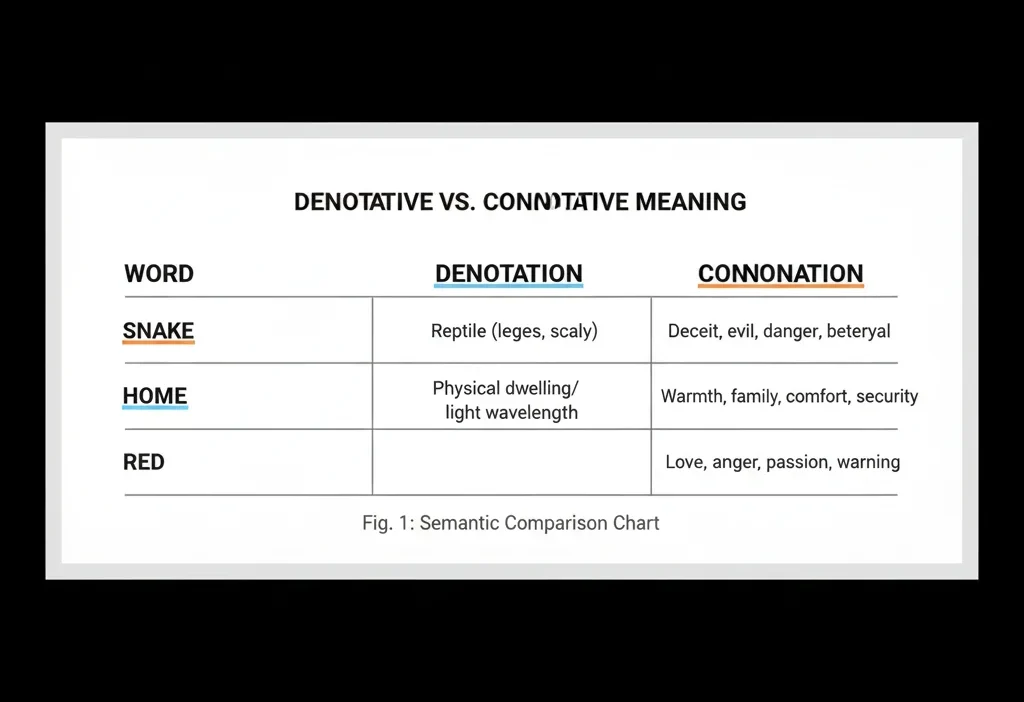
Connotative meaning refers to the emotional, cultural, or personal associations that a word carries beyond its literal definition.
In simpler terms, it’s the implied or suggested meaning behind a word — how it makes people feel or what ideas it evokes.
It’s not slang or an abbreviation — it’s a linguistic concept used in writing, literature, psychology, and communication.
🕰️ Origin and Popularity
The term “connotation” comes from the Latin word connotare, meaning “to mark along with.” It entered English usage around the 14th century, describing meanings that accompany the literal sense of a word.
Over time, linguists, poets, and educators have emphasized the importance of connotative meaning in:
- Literary analysis (understanding tone and mood)
- Advertising (choosing emotionally appealing words)
- Everyday communication (avoiding misinterpretation)
By the 20th century, it became a key concept in semiotics, linguistics, and media studies, highlighting how word choice shapes emotion and perception.

💬 Connotative Meaning in Different Contexts
Let’s see how connotative meaning works across various fields and scenarios.
🧾 In Everyday Communication
Words can evoke different feelings based on culture or experience.
Example: The word “home” denotes a place where you live but connotes warmth, safety, and belonging.
📚 In Literature and Poetry
Writers use connotation to add emotional depth or symbolism.
Example: In poetry, “winter” might connote death, loneliness, or endings.
💼 In Business and Branding
Marketers choose words with positive connotations to appeal to emotions.
Example: A brand may use “slim” instead of “skinny” to evoke confidence instead of frailty.
🧠 In Psychology or Sociology
Connotations reveal social attitudes or cultural biases.
Example: The term “childlike” has positive connotations (innocent), while “childish” sounds negative (immature).
| Context | Example Word | Denotative Meaning | Connotative Meaning |
| Everyday | “Home” | Place of residence | Warmth, love, comfort |
| Literary | “Winter” | Cold season | Endings, death, sadness |
| Business | “Affordable” | Low cost | Budget-friendly, smart choice |
| Psychology | “Childish” | Like a child | Immature or silly |
✍️ Examples of Connotative Meaning in Use
Here are a few examples to show how connotation changes tone:
Example 1:
“He’s slim.” → Positive connotation (fit, healthy)
“He’s skinny.” → Negative connotation (underweight, weak)
Example 2:
“She lives in a house.” → Neutral
“She lives in a home.” → Warm, emotional tone
Example 3:
“He’s curious.” → Positive (interested)
“He’s nosy.” → Negative (intrusive)
Example 4 (formal writing):
“The report uses persuasive language rather than manipulative language.”

🔍 Similar or Related Terms
Here are some terms closely related to connotative meaning that help expand your understanding:
| Term | Meaning |
| Denotative Meaning | The literal or dictionary definition of a word. |
| Connotation | The emotional or cultural meaning attached to a word. |
| Tone | The writer’s attitude, influenced by connotations. |
| Figurative Language | Non-literal expressions that rely on connotation (e.g., metaphors). |
These terms are often studied together in linguistics, communication, and writing classes.
✅ How to Use Connotative Meaning Correctly
Do’s:
- ✅ Consider the emotional impact of words.
- ✅ Match word connotations with your intended tone.
- ✅ Use connotation to enhance storytelling or persuasion.
Don’ts:
- ❌ Don’t assume everyone shares the same connotations — they vary by culture.
- ❌ Avoid overly negative words in sensitive contexts (e.g., “cheap” vs. “affordable”).
- ❌ Don’t confuse connotation with denotation — they work together, not interchangeably.
⚠️ Common Mistakes or Misinterpretations
- Confusing Denotation with Connotation
→ Denotation is literal; connotation is emotional. - Overgeneralizing Connotations
→ Words can carry different meanings across cultures, generations, and contexts. - Ignoring Tone
→ A single word choice can shift tone from respectful to offensive — even if technically accurate. - Using Loaded Words Unintentionally
→ In professional writing, avoid words with unintended bias or emotional weight.
❓ FAQ Section
1. What is the connotative meaning of a word?
It’s the emotional or cultural association that comes with a word, beyond its literal definition.
2. What’s the difference between denotative and connotative meaning?
Denotative refers to the dictionary meaning, while connotative refers to the implied or emotional meaning.
3. Can a word have both positive and negative connotations?
Yes. For example, “stubborn” can be negative (uncooperative) or positive (determined), depending on context.
4. Why is connotative meaning important?
It affects tone, clarity, and audience perception, especially in writing, media, and communication.
5. How do you identify connotative meaning?
Ask yourself how a word makes you feel or what images or ideas it brings to mind.
6. Is connotative meaning subjective?
Yes, it can vary by culture, age, experience, and personal values.
🪶 Conclusion
In essence, connotative meaning adds emotion and depth to language — it’s what transforms plain communication into powerful expression.
By understanding a word’s connotation, you can choose language that connects, inspires, and avoids misinterpretation.
✨ Now that you know what connotative meaning is, you’ll start to notice it everywhere — from poetry to advertising to everyday conversation. Keep exploring our site for more easy explanations of language and communication concepts

Jon McGregor is a language and word-meaning expert at Meanovia.com. He specializes in explaining complex words, phrases, and modern language trends in a clear, approachable style. His mission is to help readers quickly grasp the true meaning behind every term, making language learning and understanding effortless and engaging.